We present the Onboard Illumination Visual-Inertial Odometry (OIVIO) dataset. It consists of 36 sequences, recorded in mines, tunnels, and other dark environments, totaling more than 145 minutes of stereo camera video and IMU data. In each sequence, the scene is illuminated by an onboard light of approximately 1350, 4500, or 9000 lumens. We accommodate both direct and indirect VIO methods by providing the geometric and photometric camera calibrations. The full dataset, including sensor data, calibration sequences, and evaluation scripts can be downloaded here.
Downloads
We have organized our dataset using the Automous Systems Lab (ASL) dataset format, though our dataset additionally provides files for the photometric camera calibration and light calibration. Each sequence is available at full-resolution and separated into its own tarball.
Use the provided script to down-sample the stereo images to a desired resolution. The script requires the path to the downloaded (and extracted) sequence, output directory, and desired image size. This script additionally updates the camera intrinsics according to the new image resolution.
python downsample_asl.py --src path/to/TN_015_HH_01 --dst path/to/output --size 640x480
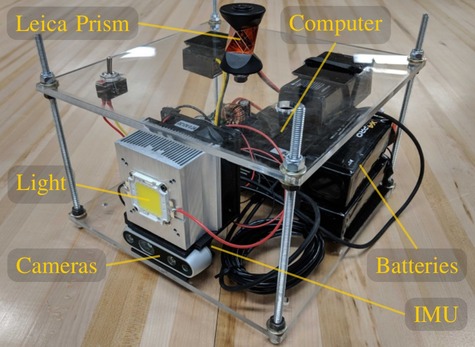
Sensor Rig
We capture inertial data with LORD Microstrain 3DM-GX5-15 at 100Hz, and stereo pair of 1280x720, grayscale images with a Intel RealSense D435i at 30Hz. Each sequence in our benchmark is illuminated by an onboard, maximum 9000 lumens, 100W, white LED light. Using this sensor setup, as seen in the image below, we attempt to capture the same trajectory three times, modulating the light’s intensity to approximately 100, 50, and 15 percent of its full capacity.
Evaluation
This benchmark provides two methods for ground-truthing. The three sequences where the ground-vehicle is used, 3D positions at 10Hz were captured via a Leica TCRP1203 R300. In all remaining sequences, we start and end in the same position, permitting the use of total accumulated drift as another evaluation metric. We provide the following scripts for evaluation, adapted from the TUM benchmark tools.
Calibration
We additionally provide all calibration datasets, so that custom calibration models may be inferred. The majority of the calibration sequences employ the Calibu calibration target.
CITATION
If you use this benchmark in your research, please cite the following paper:
M. Kasper, S. McGuire, C. Heckman, “A Benchmark for Visual-Inertial Odometry Systems Employing Onboard Illumination”, Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2019. [Bibtex]