RMap: Millimeter-Wave Radar Mapping Through Volumetric Upsampling
Ajay N. Mopidevi
Kyle Harlow
Chris Heckman
Millimeter Wave Radar is being adopted as a viable alternative to lidar and radar in adverse visually degraded conditions, such as in the presence of fog and dust. However, this sensor modality suffers from severe sparsity and noise under nominal conditions, which makes it difficult to use in precise applications such as mapping. This work presents a novel solution to generate accurate 3D maps from sparse radar point clouds. RMap uses a generative transformer architecture which upsamples, denoises, and fills the incomplete radar maps to resemble lidar maps. We test this method on the ColoRadar dataset to demonstrate its efficacy.
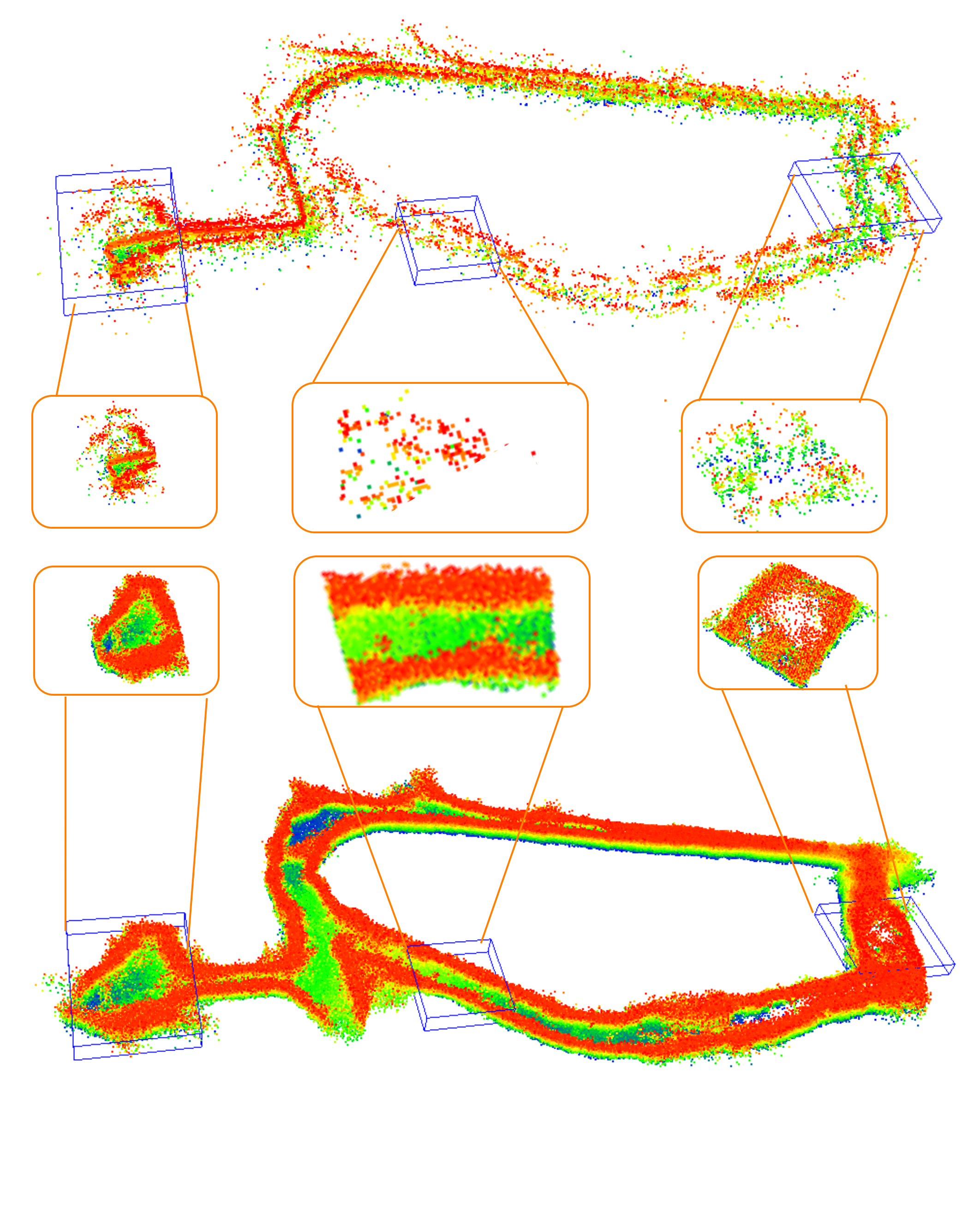
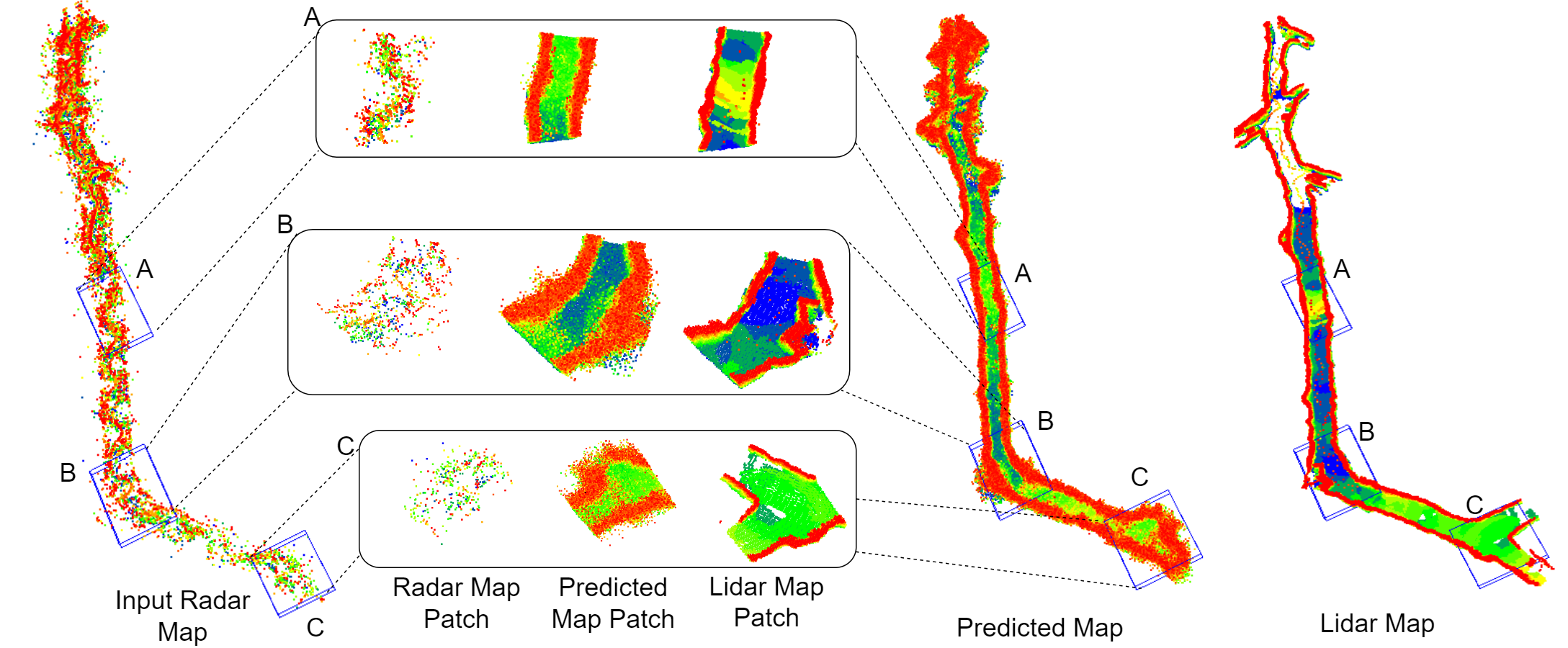
Method
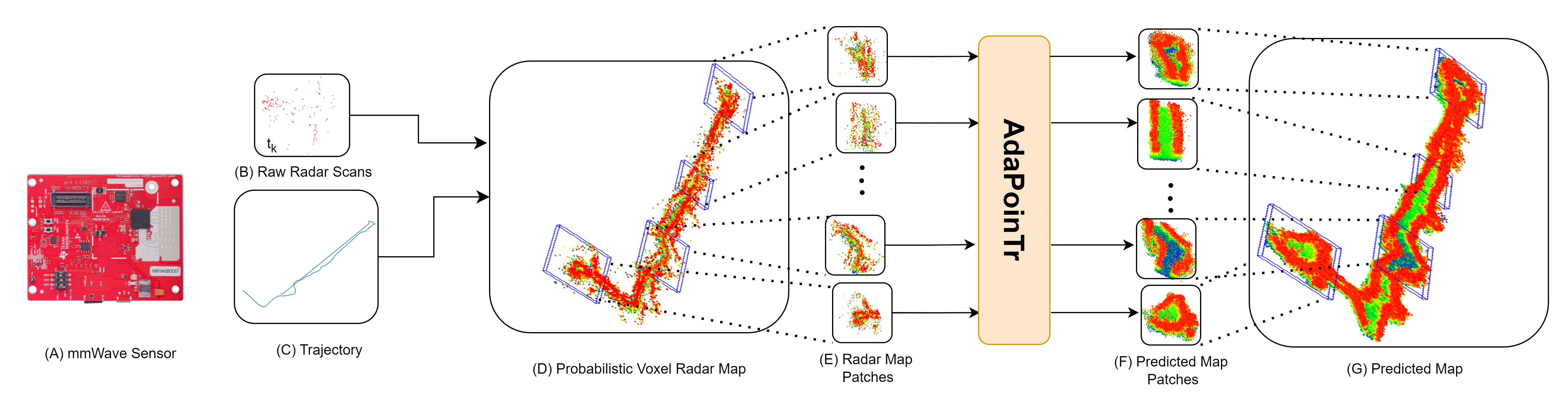
An (A) automotive-grade system-on-chip mmWave radar sensor produces (B) Radar point clouds generated by CFAR thresholding along a trajectory (C). A (D) Radar Map is generated using the radar point clouds with Radar Octomap along the trajectory of the robot, with different pose locations highlighted. This map is then divided into (E) Patches of size 2048 sampled at different locations along the trajectory. These patches are passed through the pointcloud completion network, AdaPoinTr, to produce (F) predicted map patches. The predicted point clouds of size 8192 from AdaPoinTr are then merged into (G) the final predicted radar map.
Presentation Video
Citation
@article{mopidevi2023rmap,
title={RMap: Millimeter-Wave Radar Mapping Through Volumetric Upsampling},
author={Mopidevi, Ajay Narasimha and Harlow, Kyle and Heckman, Christoffer},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.13188},
year={2023}
}